|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6-Cd8atm1(CD8A)BcgenCd8btm1(CD8B)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hCD8 mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6
|
Catalog number
|
112811
|
Aliases
|
CD8, p32, Leu2, IMD116, CD8alpha;
LY3, P37, LEU2, LYT3, Ly-3, CD8B1, CD8beta
|
Description
-
The CD8 antigen is a cell surface glycoprotein found on most cytotoxic T lymphocytes that mediates efficient cell-cell interactions within the immune system. The CD8 antigen acts as a coreceptor with the T-cell receptor on the T lymphocyte to recognize antigens displayed by an antigen presenting cell in the context of class I MHC molecules. The coreceptor functions as either a homodimer composed of two alpha chains or as a heterodimer composed of one alpha and one beta chain. Both alpha and beta chains share significant homology to immunoglobulin variable light chains.
-
The exons 1-3 and partial exon 4 of mouse Cd8a gene that encode the extracellular domain were replaced by human CD8A exons 1-3 and partial exon 4 in B-hCD8 mice. The exons 1-3 and partial exon 4 of mouse Cd8b1 gene that encode the extracellular domain were replaced by human CD8B exons 1-3 and partial exon 4 in B-hCD8 mice.
-
Mouse CD8 was only detectable in wild type C57BL/6JNifdc mice. Human CD8 was detectable in homozygous B-hCD8 mice but not in wild type mice.
-
B-hCD8 mice have normal T cell immunogenic function induced by OVA.
Targeting strategy
Gene targeting strategy for B-hCD8 mice. The exons 1-3 and partial exon 4 of mouse Cd8a gene that encode signal peptide and extracellular domain are replaced by human counterparts in B-hCD8 mice. The genomic region of mouse Cd8a gene that encodes transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic portion is retained. The promoter and 5’UTR region of the mouse Cd8a gene are replaced by human counterparts. The chimeric CD8A expression is driven by human CD8A promoter, while mouse Cd8a gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
The exons 1-3 and partial exon 4 of mouse Cd8b1 gene that encode signal peptide and extracellular domain are replaced by human counterparts in B-hCD8 mice. The genomic region of mouse Cd8b1 gene that encodes transmembrane domain and cytoplasmic portion is retained. The promoter and 5’UTR region of the mouse Cd8b1 gene are replaced by human counterparts. The chimeric CD8B1 expression is driven by human CD8B1 promoter, while mouse Cd8b1 gene transcription and translation will be disrupted.
Protein expression analysis in spleen
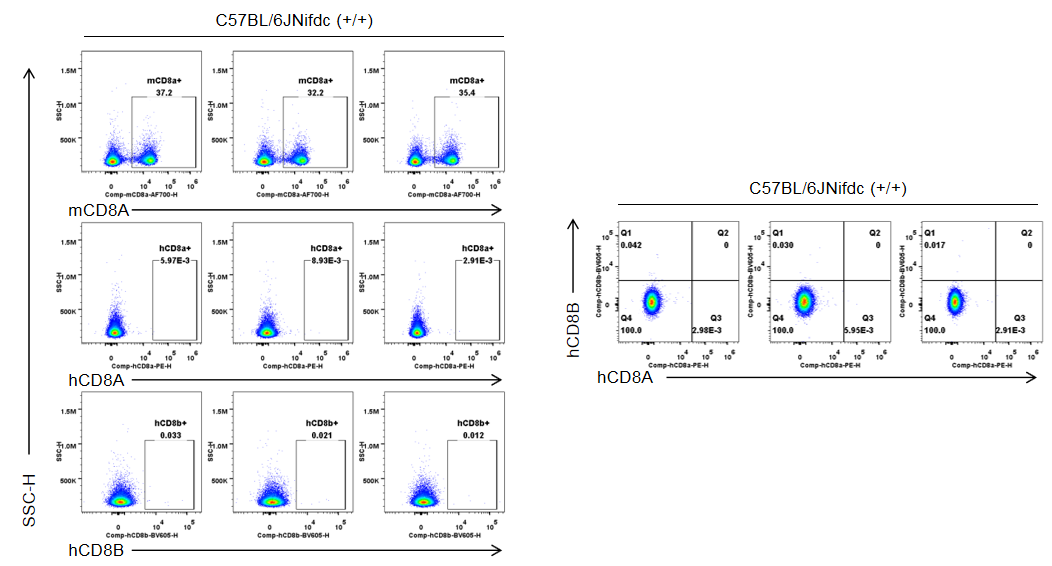
Strain specific CD8 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD8 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD8 mice (H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD8 antibody (anti-human CD8A, Biolegend, 300908; anti-mouse CD8A, Biolegend, 100730; anti-human CD8B, BD, 742392). Mouse CD8A was detectable in wild-type mice.
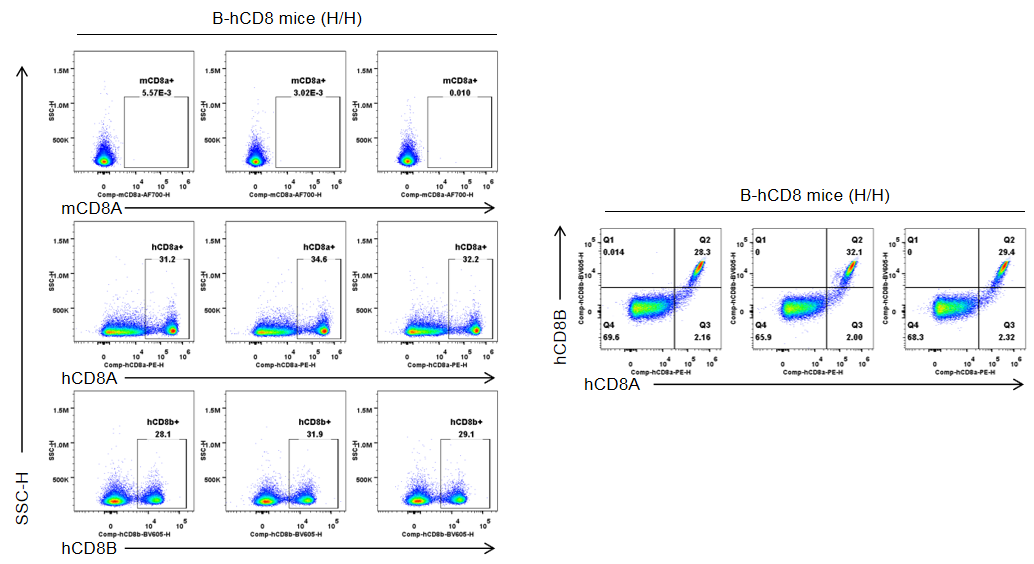
Strain specific CD8 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD8 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD8 mice (H/H), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD8 antibody (anti-human CD8A, Biolegend, 300908; anti-mouse CD8A, Biolegend, 100730; anti-human CD8B, BD, 742392). Human CD8A and human CD8B was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hCD8 mice but not in wild-type mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the spleen of C57BL/6JNifdc mice
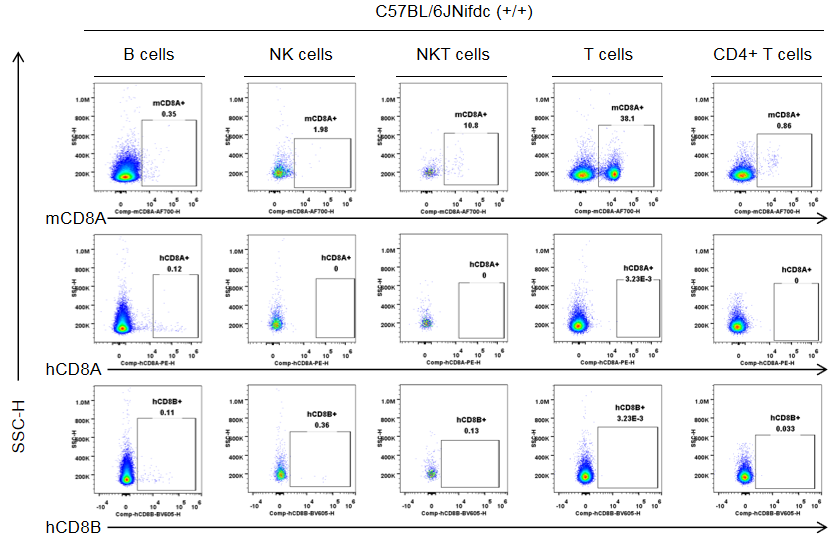
Strain specific CD8 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+, female, n=3, 9-week-old), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD8 antibody (anti-human CD8A, Biolegend, 300908; anti-mouse CD8A, Biolegend, 100730; anti-human CD8B, BD, 742392). Mouse CD8A was detectable in NKT cells and T cells from wild-type mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the spleen of B-hCD8 mice
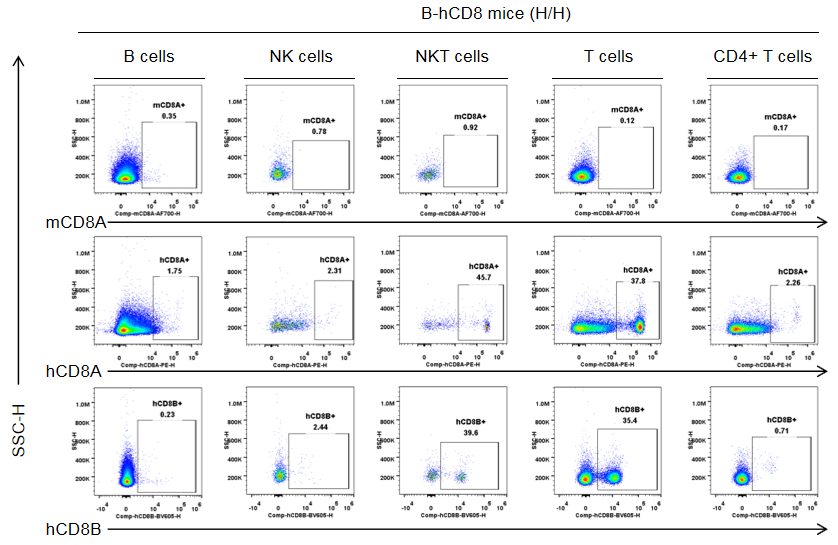
Strain specific CD8 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD8 mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from homozygous B-hCD8 mice (H/H, female, n=3, 9-week-old), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD8 antibody (anti-human CD8A, Biolegend, 300908; anti-mouse CD8A, Biolegend, 100730; anti-human CD8B, BD, 742392). Human CD8A and CD8B were detectable in NKT cells and T cells from B-hCD8 mice, but not in the wild-type mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the blood of C57BL/6JNifdc mice
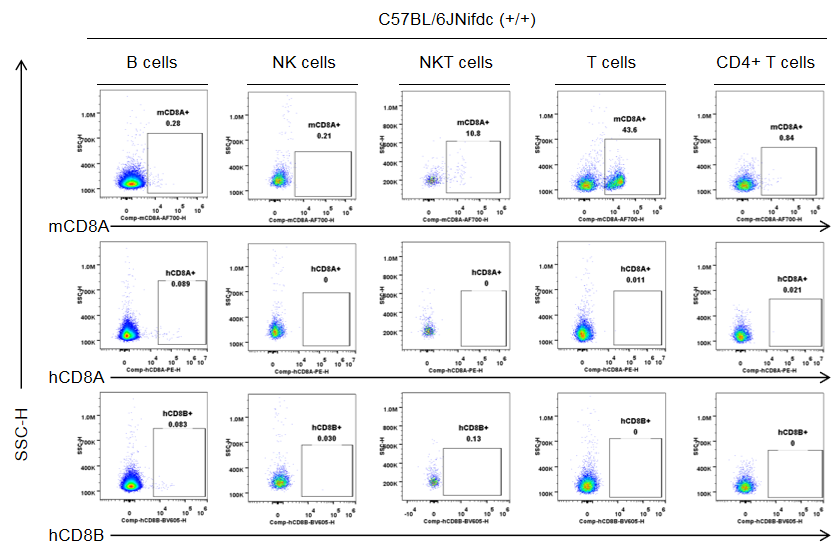
Strain specific CD8 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc by flow cytometry. Blood cells were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+, female, n=3, 9-week-old), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD8 antibody (anti-human CD8A, Biolegend, 300908; anti-mouse CD8A, Biolegend, 100730; anti-human CD8B, BD, 742392). Mouse CD8A was detectable in NKT cells and T cells from wild-type mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the blood of B-hCD8 mice
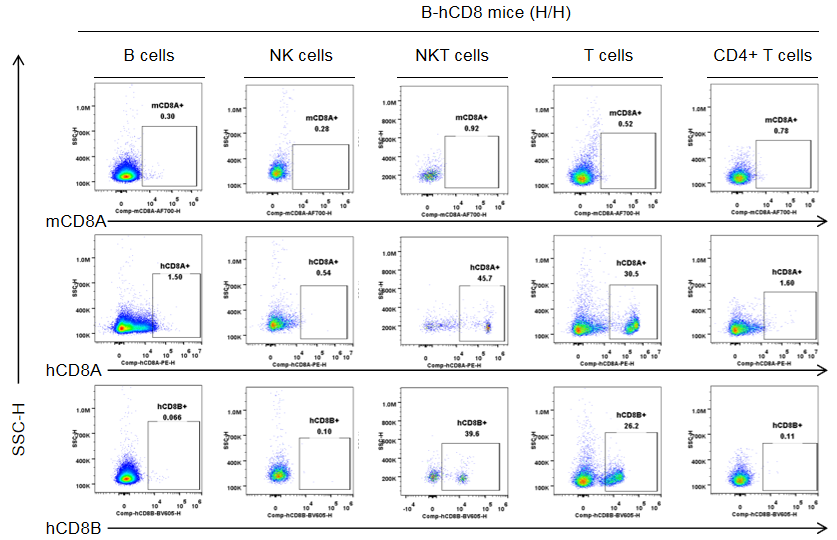
Strain specific CD8 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD8 mice by flow cytometry. Blood cells were collected from homozygous B-hCD8 mice (H/H, female, n=3, 9-week-old), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD8 antibody (anti-human CD8A, Biolegend, 300908; anti-mouse CD8A, Biolegend, 100730; anti-human CD8B, BD, 742392). Human CD8A and CD8B were detectable in NKT cells and T cells from B-hCD8 mice, but not in the wild-type mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the lymph node of C57BL/6JNifdc mice
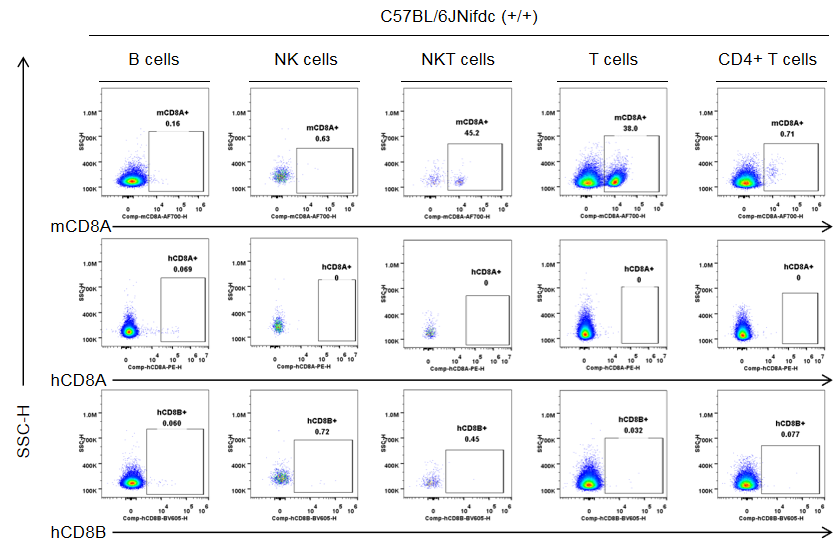
Strain specific CD8 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc by flow cytometry. The lymph nodes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (+/+, female, n=3, 9-week-old), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD8 antibody (anti-human CD8A, Biolegend, 300908; anti-mouse CD8A, Biolegend, 100730; anti-human CD8B, BD, 742392). Mouse CD8A was detectable in NKT cells and T cells from wild-type mice.
Protein expression in different immune cells of the lymph node of B-hCD8 mice
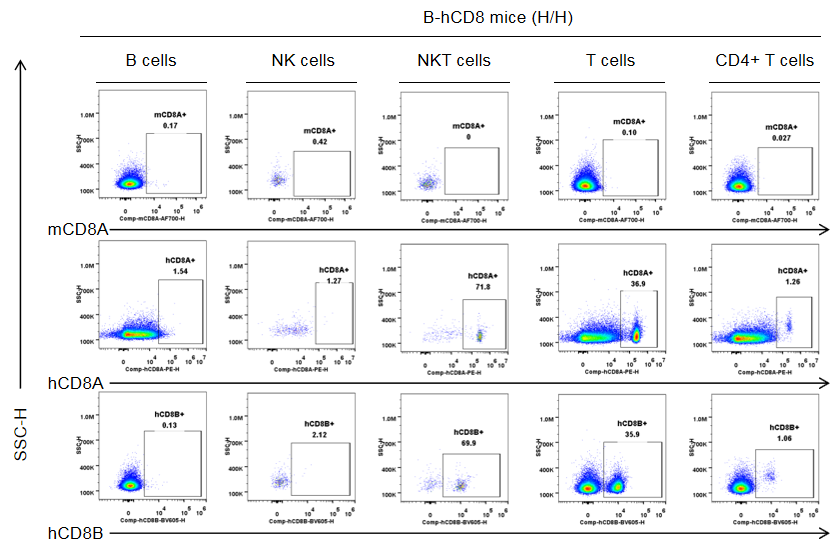
Strain specific CD8 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD8 mice by flow cytometry. The lymph nodes were collected from homozygous B-hCD8 mice (H/H, female, n=3, 9-week-old), and analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD8 antibody (anti-human CD8A, Biolegend, 300908; anti-mouse CD8A, Biolegend, 100730; anti-human CD8B, BD, 742392). Human CD8A and CD8B were detectable in NKT cells and T cells from B-hCD8 mice, but not in the wild-type mice.
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the spleen
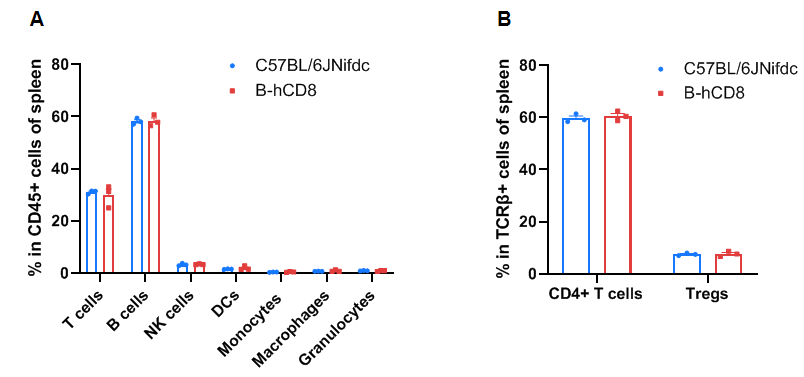
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and homozygous B-hCD8 mice (female, 9-week-old, n=3). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Frequencies of T cells, B cells, NK cells, DCs, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs in B-hCD8 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that humanization of CD8 does not change the frequency or distribution of these cell types in the spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the blood
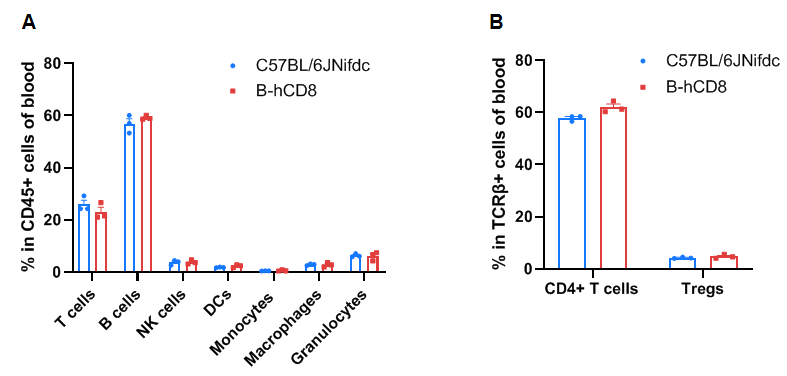
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the blood by flow cytometry. Blood cells were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (female, 9-week-old, n=3) and homozygous B-hCD8 mice (female, 9-week-old, n=3). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the blood cells was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Frequencies of T cells, B cells, NK cells, DCs, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs in B-hCD8 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6JNifdc mice, demonstrating that humanization of CD8 does not change the frequency or distribution of these cell types in the blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the lymph node

Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in the lymph nodes by flow cytometry. The lymph node cells were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice (female, 9-week-old, n=3) and homozygous B-hCD8 mice (female, 9-week-old, n=3). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the lymph node cells was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Frequencies of T cells, B cells, NK cells, CD4+ T cells, and Tregs in B-hCD8 mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that humanization of CD8 does not change the frequency or distribution of these cell types in the lymph nodes. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
The OVA induced immune responses in B-hCD8 mice
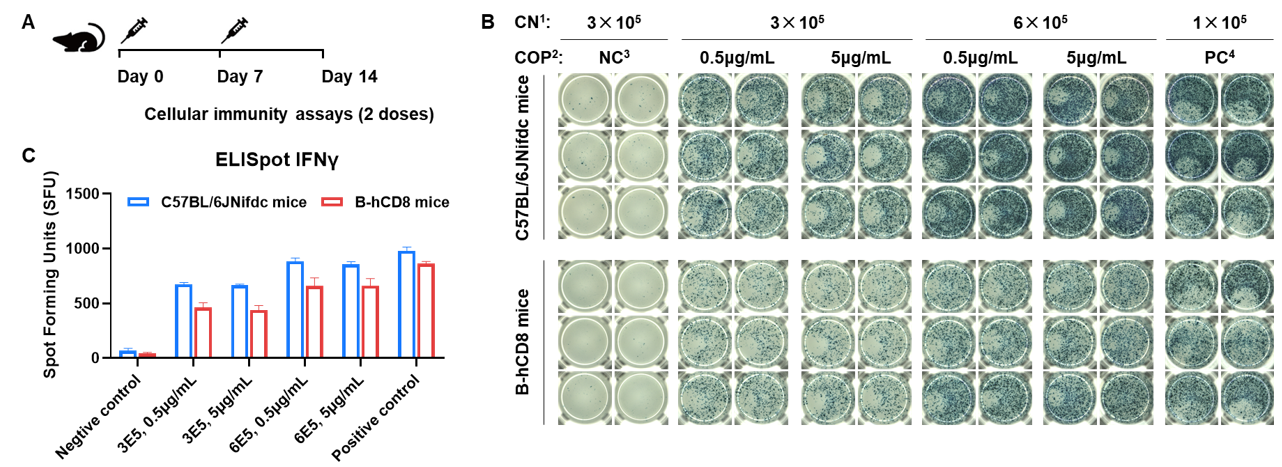
Detection of OVA-induced immune responses in B-hCD8 mice by IFN-γ ELISpot assay. (A) Scheme of OVA immunization and testing. Female wild-type C57BL/6JNifdc mice and B-hCD8 mice at the age of 9–10 weeks were immunized with intraperitoneal injection of 0.5 mg of OVA protein (Simga, A5503-25MG) and 50 μg poly (I:C) (InvivoGen, tlrl-pic). Mice were immunized with OVA two times at 1-week interval. One week after the last immunization, mice were sacrificed. The splenocytes were extracted, stimulated with OVA peptide257–264, or no peptide as negative control (NC), or Cell Activation Cocktail (without Brefeldin A), (Biolegend, 42330) as positive control, and then measured for IFN-γ secretion. No significant difference in body weight among groups (Data was not shown). (B) Representative results showing stimulation of splenocytes harvested from immunized mice with negative control, or OVA peptide257–264, or positive control in duplicates. (C) Summary of results. These data indicate that B-hCD8 mice have normal T cell immunogenic function. 1, CN: Cell number. 2, COP: Concentration of the peptide. 3, NC: negative control. 4, PC: positive control.