B-hCD24 mice plus
| Non-disclosure |
Non-disclosure
|
Common Name | B-hCD24 mice plus |
| Background | C57BL/6N | Catalog number | 111953 |
|
Related Genes |
CD24, CD24A, PRO940 | ||
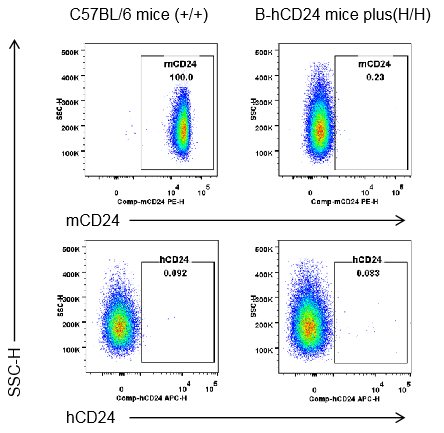
Strain specific CD24 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus by flow cytometry. Red blood cells were collected from wild-type mice (+/+), homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD24 antibody. Mouse CD24 was detectable in wild-type mice, but not detectable in B-hCD24 mice plus. Human CD24 was not detectable in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus.
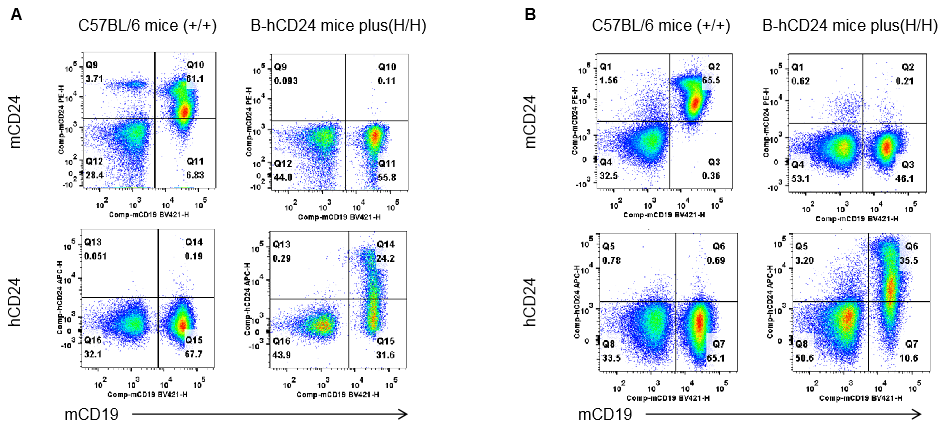
Strain specific CD24 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus by flow cytometry. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD24 antibody. Mouse CD24 was detectable in wild-type mice blood(A) and spleen(B). Human CD24 was detectable in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus blood(A) and spleen(B).
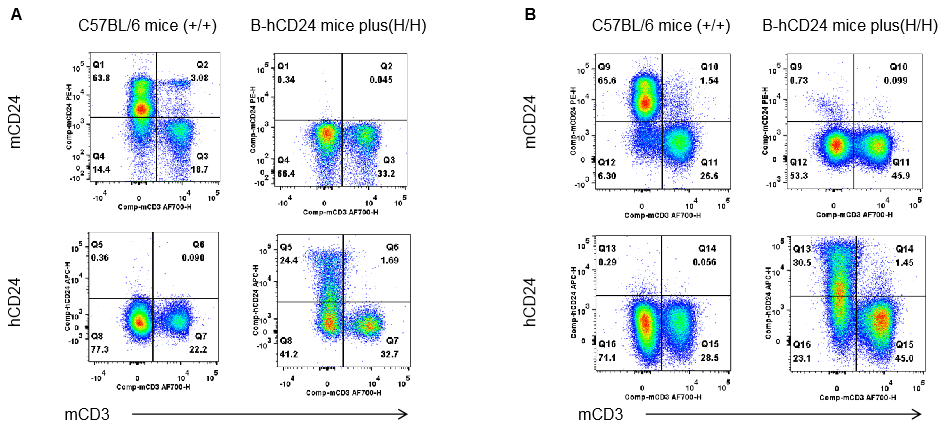
Strain specific CD24 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus by flow cytometry. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD24 antibody. Mouse CD24 was weakly detectable in wild-type mice blood(A) while mouse CD24 can not be detected in wild-type mice spleen(B). Human CD24 was not detectable in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus blood(A) and spleen(B).
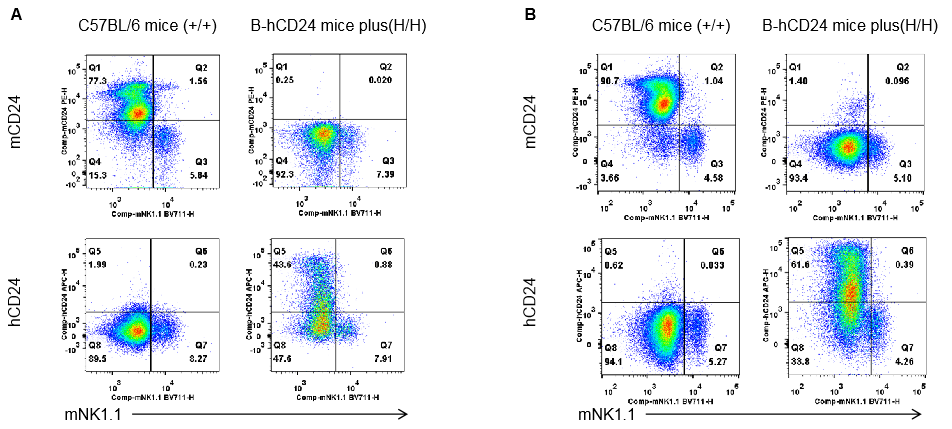
Strain specific CD24 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus by flow cytometry. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD24 antibody. Mouse CD24 was not detectable in wild-type mice blood(A) and spleen(B). Human CD24 was not detectable in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus blood(A) and spleen(B).
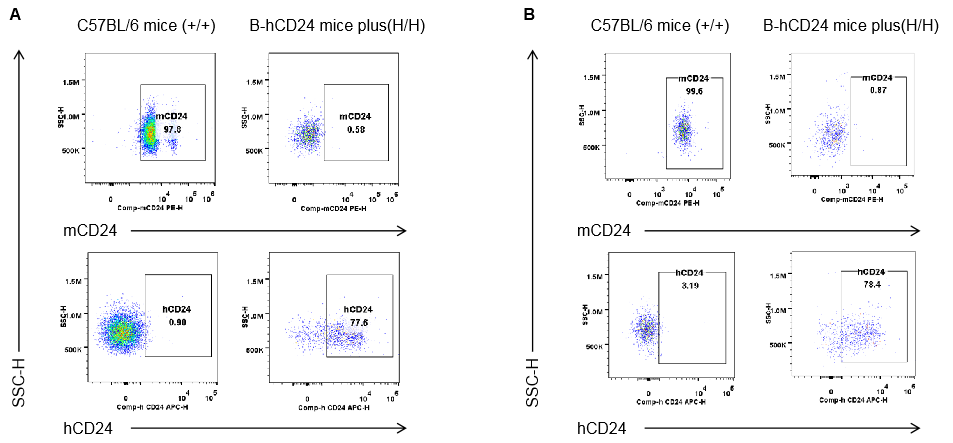
Strain specific CD24 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus by flow cytometry. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD24 antibody. Mouse CD24 was detectable in wild-type mice blood(A) and spleen(B). Human CD24 was detectable in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus blood(A) and spleen(B).
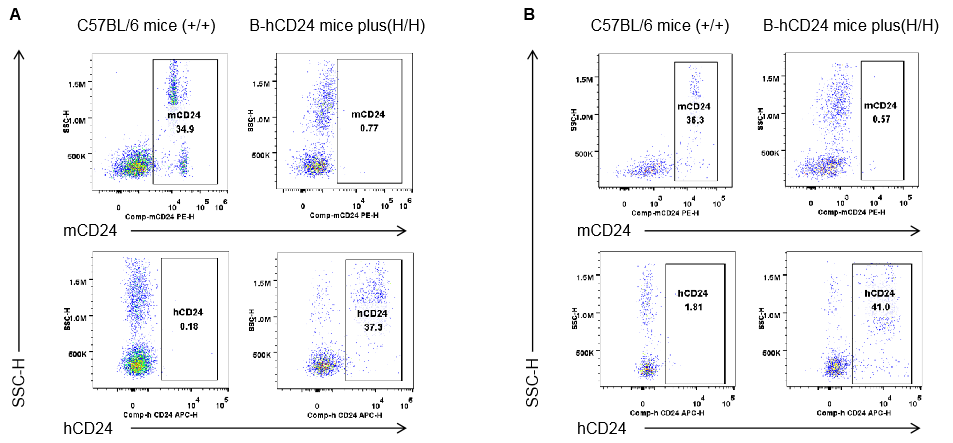
Strain specific CD24 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus by flow cytometry. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD24 antibody. Mouse CD24 was detectable in wild-type mice blood(A) and spleen(B). Human CD24 was detectable in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus blood(A) and spleen(B).
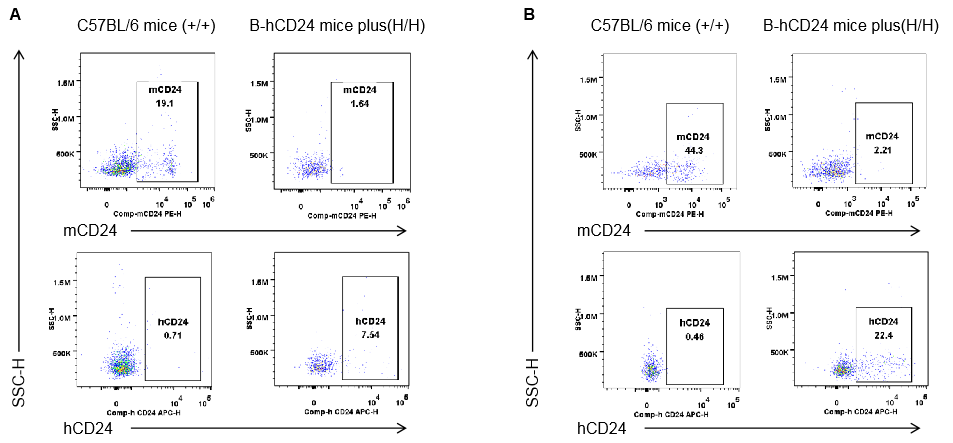
Strain specific CD24 expression analysis in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus by flow cytometry. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from wild-type mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-CD24 antibody. Mouse CD24 was detectable in wild-type mice blood(A) and spleen(B). Human CD24 was detectable in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus blood(A) and spleen(B).
Antibody binding assay-the Ab1
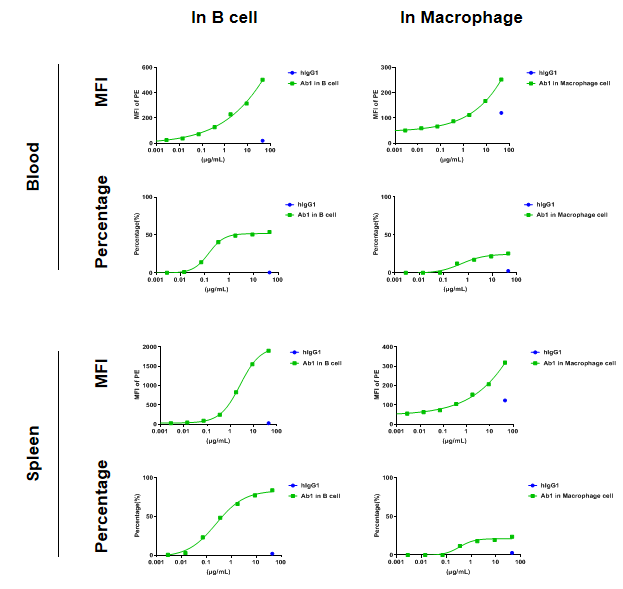
Analysis of blood and splenocytes of B-hCD24 mice plus by FACS. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus. Flow cytometry analysis of the blood and splenocytes were performed to assess anti-human CD24 antibody Ab1 binding with B cell and macrophages. B cell and macrophages in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus bind well with Ab1 vs isotype control. (All antibodies were provided by client)
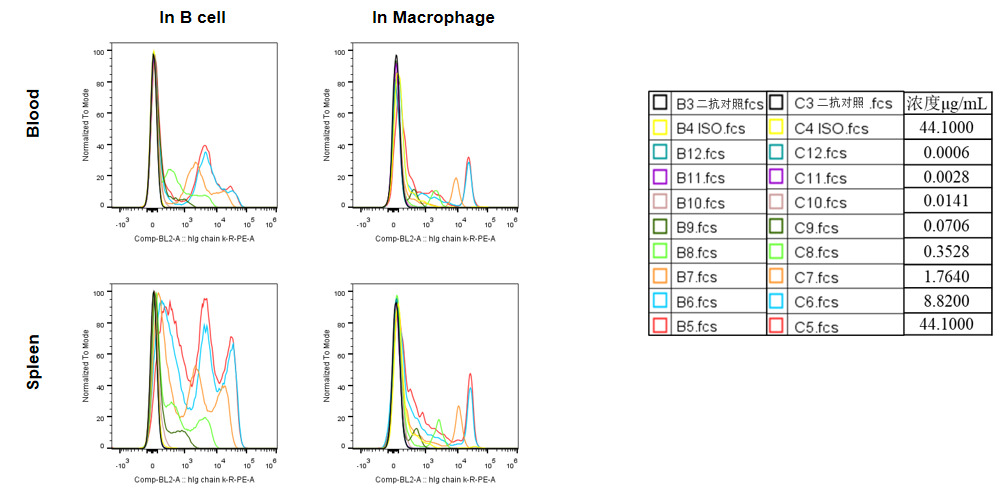
Analysis of blood and splenocytes of B-hCD24 mice plus by FACS. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus. Flow cytometry analysis of the blood and splenocytes were performed to assess anti-human CD24 antibody Ab1 binding with B cell and macrophages. B cell and macrophages in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus bind well with Ab1 vs isotype control. (All antibodies were provided by client)
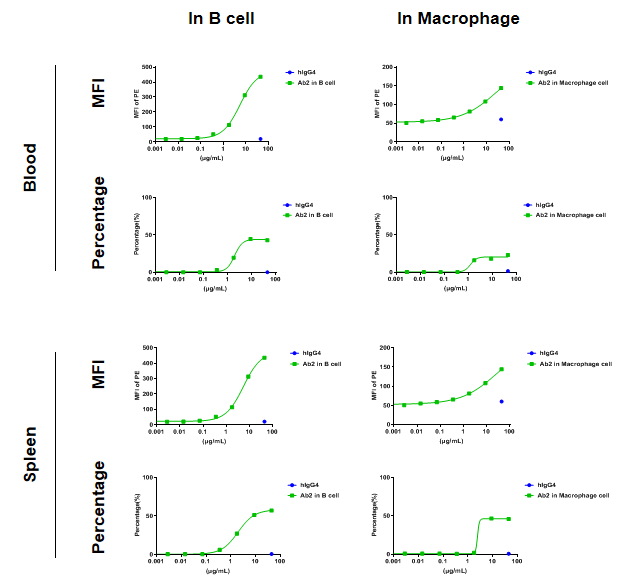
Analysis of blood and splenocytes of B-hCD24 mice plus by FACS. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus. Flow cytometry analysis of the blood and splenocytes were performed to assess anti-human CD24 antibody Ab1 binding with B cell and macrophages. B cell and macrophages in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus bind well with Ab2 vs isotype control. (All antibodies were provided by client)
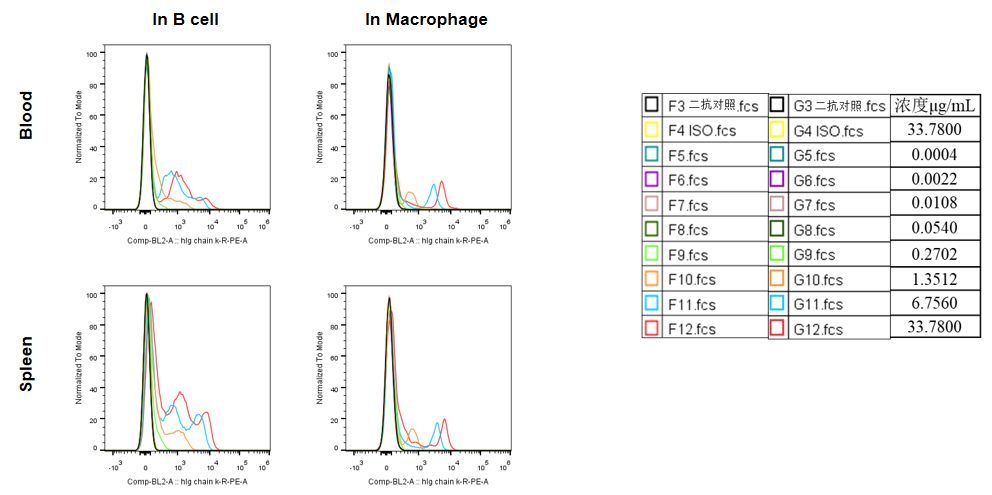
Analysis of blood and splenocytes of B-hCD24 mice plus by FACS. Blood cells and splenocytes were collected from homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus. Flow cytometry analysis of the blood and splenocytes were performed to assess anti-human CD24 antibody Ab2 binding with B cell and macrophages. B cell and macrophages in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus bind well with Ab2 vs isotype control. (All antibodies were provided by client)
Analysis of spleen leukocytes subpopulation in B-hCD24 mice plus
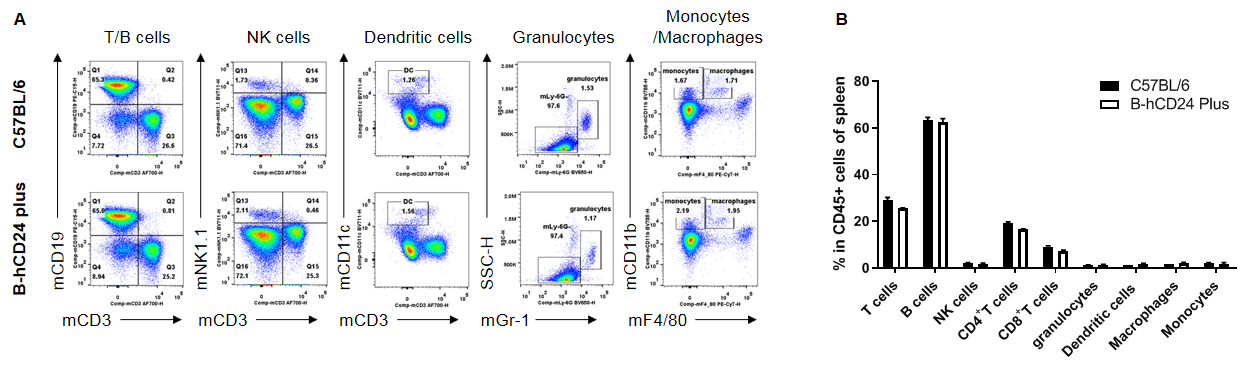
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from male C57BL/6 and B-hCD24 mice plus (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CD24 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
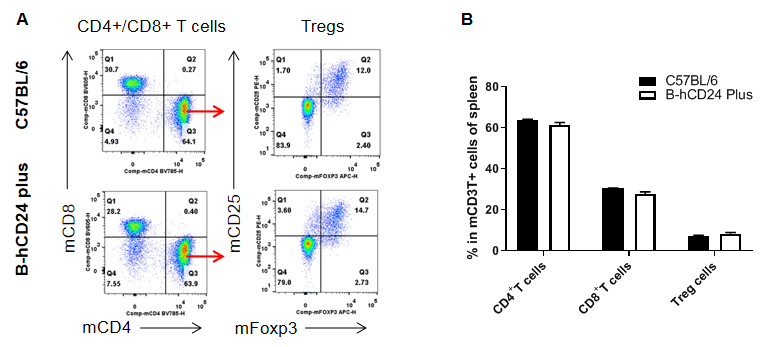
Analysis of spleen T cell subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from male C57BL/6 and B-hCD24 mice plus(n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for CD3+ T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. The percent of CD8+ T cells , CD4+ T cells and Tregs in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CD24 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
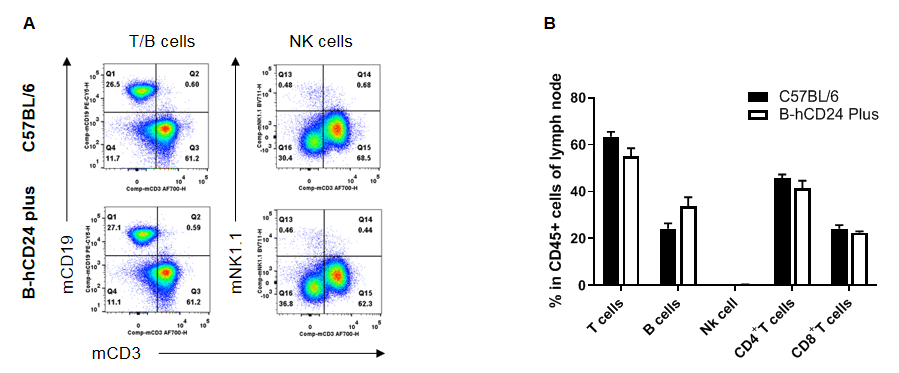
Analysis of lymph node leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Leukocytes were isolated from male C57BL/6 and B-hCD24 mice plus (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CD24 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in lymph node. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
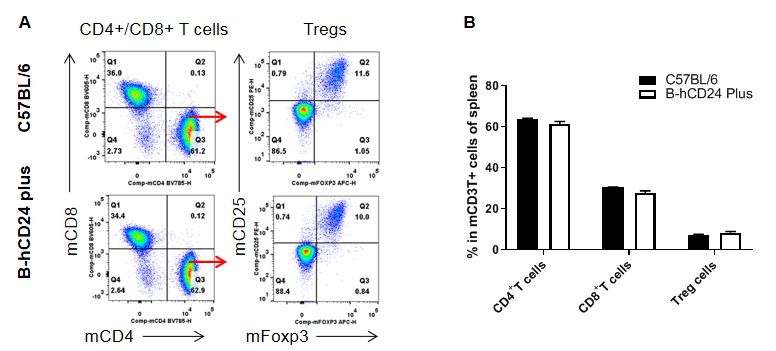
Analysis of lymph node T cell subpopulations by FACS. Leukocytes were isolated from male C57BL/6 and B-hCD24 mice plus(n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for CD3+ T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. The percent of CD8+ T cells , CD4+ T cells and Tregs in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CD24 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in lymph node. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
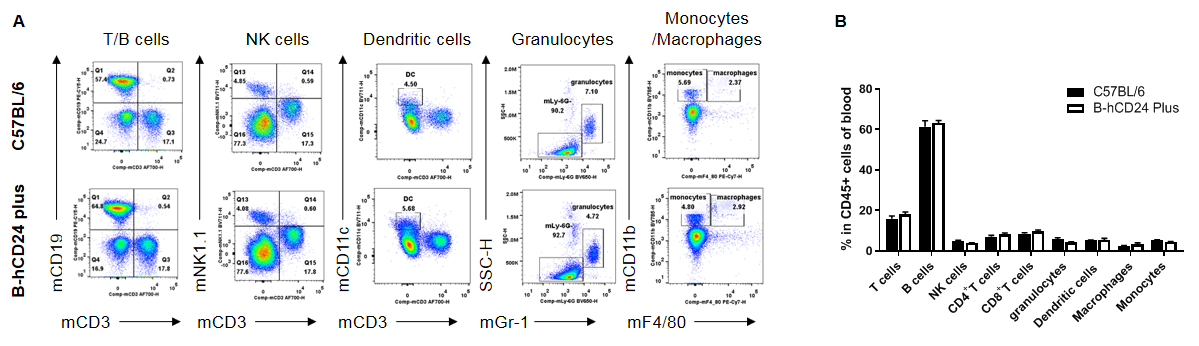
Analysis of blood leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Blood cells were isolated from male C57BL/6 and B-hCD24 mice plus (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes and macrophages in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CD24 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
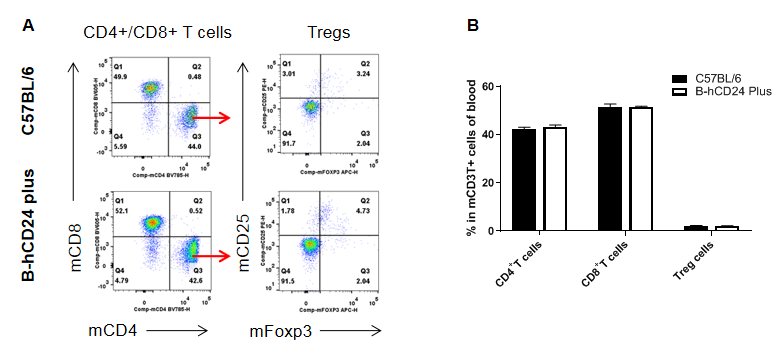
Analysis of blood T cell subpopulations by FACS. Blood cells were isolated from male C57BL/6 and B-hCD24 mice plus(n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live CD45+ cells were gated for CD3+ T cell population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. The percent of CD8+ T cells , CD4+ T cells and Tregs in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CD24 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes in blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
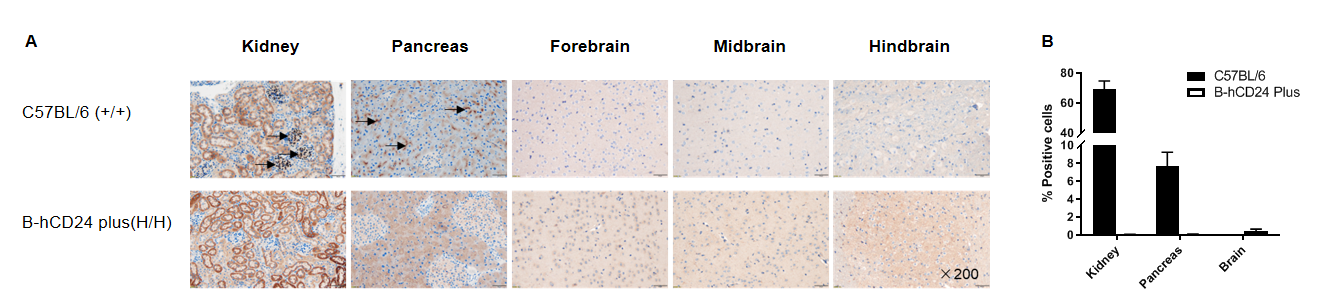
Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of CD24 expression in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus. The kidney, pancreas and brain were collected from WT and homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus and analyzed by IHC with anti-mouse CD24 and anti-human CD24 respectively. Human CD24 was not detectable in the kidney, pancreas and brain. Mouse CD24 was detectable in the glomeruli and pancreatic exocrine adenocyte membrane (Black arrow) while not in the renal tubule, pancreas islet or brain.
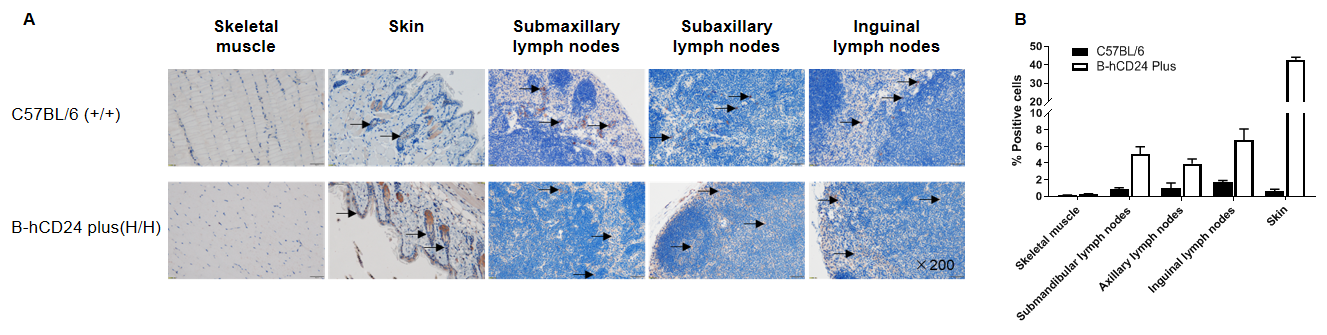
Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of CD24 expression in homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus. The skeletal muscle, skin, submaxillary lymph nodes, subaxillary lymph nodes and inguinal lymph nodes were collected from WT and homozygous B-hCD24 mice plus and analyzed by IHC with anti-mouse CD24 and anti-human CD24 respectively. Human CD24 was detectable in the skin, submaxillary lymph nodes, subaxillary lymph nodes and inguinal lymph nodes (Black arrow) while not in the skeletal muscle. Mouse CD24 was detectable in the skin, submaxillary lymph nodes, subaxillary lymph nodes and inguinal lymph nodes (Black arrow) while not in the skeletal muscle.